In part 4 of our series, we discuss the digitalization of promotions and take a closer look at the importance of developing a digital environment for promotions management.
The Middle East has experienced significant growth in internet penetration in recent years, with increasing numbers of people gaining access to the internet through smartphones and other devices. A significant portion of the population is young, with a high proportion of tech-savvy individuals who are active users of social media and other digital platforms. This widespread connectivity provides an opportunity for companies to reach a larger audience through digital channels.
It’s therefore not surprising that the region has witnessed a surge in ecommerce activity. Here, digital promotions play a crucial role in driving traffic to ecommerce platforms and encouraging online purchases. Companies are increasingly adopting a mobile-first approach to their marketing strategies, including digital promotions optimized for smartphones and tablets.
In our last article, we discussed the phenomenon of value-destroying promotions: Based on our experience in optimizing promotions in the FMCG industry, typically 30 to 40 percent of promotions are “value destroyers”, yielding a negative ROI with limited volume impact. This is mainly due to the fact that companies often neglect the importance of developing an integrated data ecosystem for promotion management, allowing them to collect and analyze data and effectively manage promotions.
Today’s world is undeniably digital. Top-performing companies have understood that making good use of data is key to success and that effective promotions management starts with data collection and building a database to optimize future promotions.
Successful promotion management needs reliable data
Many companies still count on a manual process based on intuition and past experience to decide on how, when, and which type of promotion to launch. This is of course much more error-prone than a data-based approach. Comprehensive data ecosystems enable companies to store and analyze important information about their past, current, and potential future promotions.
From experience, we consider data and analytics the most important advancement in the promotion space because they lay the foundation for actionable insights and successful campaigns. Whenever we start working with our clients on promotion optimization projects, the first step we take is a due diligence investigation to understand their current promotion data ecosystem.
Essential elements of your promotion database
We have identified four key data sources that build the foundation of every promotion database, enabling companies to measure the effectiveness and efficiency of promotions.
- Promotion depth, type, timing, and frequency
The database should be organized on a product level and should contain the following variables: the discount level, which is key for identifying the depth required to trigger a purchase, the offer type, which illustrates how the discount should be communicated to consumers (i.e. bundle, price off, coupons), the timing, which is based on identifying the best occasion for launching promotions (i.e. week type and seasonality), and finally, the frequency of promotions, which indicates how often promotions have been launched during a given timeframe.
- Price and costs
Product price and cost is critical to control profitability, but also to track how these parameters change over time to adapt promotion calendars accordingly. Recording the direct promotion costs (i.e. slot fees, secondary displays, and other fees paid to retailers) allows to estimate the absolute promotion profitability.
- Sell-out volume
The sell-out volume is defined as the quantity sold directly to consumers. It is typically provided by the retailers, for example as part of the yearly trade agreements, with updates on a weekly or monthly basis.
Sell-out data is a better indicator for promotion optimization than sell-in data, providing information on the quantity sold from producer to retailer. Direct sales data without a time-lag enables you to measure the impact of all promotion elements surrounding consumer purchase intention with higher accuracy (promo mechanics, execution, communication, promotions from competitors, etc.).
- Execution details
The way promotions are executed play a key role for consumers’ purchasing behavior. It is therefore important to incorporate data on accompanying activities for promotions. Promotional activities are usually supported with Above-the-Line (ATL) measures like internet advertisements, banners, and leaflets, as well as Below-the-Line (BTL) measures that target a specific group of customers through email campaigns, coupons, and in-store efforts.
Comprehensive promotion management in six steps
Our experience shows that companies often fail to craft a holistic promotion strategy by defining their objective, designing their analytic-fed data ecosystem, and successfully optimizing and tracking promotion efficiency and effectiveness. For successful promotion management, we suggest following the framework below, which is comprised of six main pillars.
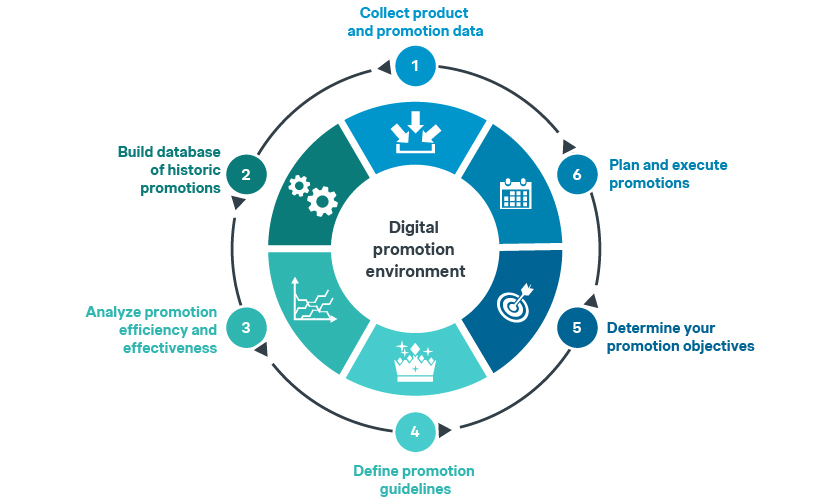
1. Collect product and promotion data:
Past promotions data should be gathered and collected, e.g. product price and cost, promo cost, volume uplift, promo type, frequency, discount, timing, etc.
2. Build database of historic promotions:
A robust database of historic promotions is then developed and should be constantly updated.
3. Analyze promotion efficiency and effectiveness:
The data needs to be analyzed in a two-step process: first, conduct a statistical modeling analysis focused on enhancing the efficiency of promotions. Next, dissect the effectiveness of past promotions to distinguish between effective and profitable vs. ineffective and unprofitable promotions.
4. Define promotion guidelines:
Following the analysis process, and relying on the generated insights, detailed promotion guidelines are defined, dictating how, when, and which product to promote.
5. Determine your promotion objectives:
Companies should clearly define what they want to achieve with their promotions through tactical or strategic objectives.
6. Plan and execute promotions:
Make sure that promotions are executed as per the plan, deploying sufficient resources to control the activities in the stores.
Harnessing the power of Machine Learning for promotion predictability
Machine learning brings excellent improvement opportunities to the promotion space. Depending on organization’s current status, you can choose between three approaches to build your promotion database:
- Static excel integrated database with manual updating
- IT integrated database (e.g. Enterprise resource planning – ERP)
- A high-performance analytical platform database, where Machine Learning algorithms are applied to derive insights and actionable recommendations for promotion optimization (i.e. optimal promotion type, time, and product) and give precise forecasts on promotion volume uplift and ROI
Digital promotion management improves promotion efficiency and effectiveness
In today’s digital world, comprehensive databases covering the above-mentioned areas are key to successful promotions management and deliver a huge competitive advantage. Following the presented six-step approach will significantly boost your promotion efficiency and effectiveness. In recent years, we have conducted several projects where we applied Machine Learning and advanced analytics to identify suitable products for promotions and generate accurate promotion uplift predictions.
Reach out to Lovrenc Kessler to learn more.
Read more from our promotional effectiveness series in the Middle East:
Part 2: The 7 drivers of effective sales promotions in the UAE
Part 3: Promotion effectiveness in MENA: How to fix the 30 percent of value-destroying promotions
Part 4: Digital promotions in MENA: Advantages of promotion database management
Part 5: 5 rules for producers and retailers to jointly build customer-centric promotions
Part 6: Promotion effectiveness in MENA: How do promotions change shopper behavior in the long term?








