China’s 2020 NRDL (National Reimbursement Drug List) results are out, marking many firsts in history. In this article, we revisit the three themes and five predictions from our NRDL perspectives last October, and cordially invite you for a quick survey on its future outlook.
China doesn’t take a break over Christmas, which works out well for the NHSA (National Health Security Administration). On December 28 2020, the NHSA released the much-awaited official results of the latest NRDL update.
As expected, the 2020 NRDL marked several firsts in history,
- For the very first time, there were around 700 drugs going into the process;
- Subsequently, 162 drugs made it into the shortlist, and 119 of them eventually made the listing, breaking the record for most inclusions in NRDL history;
- Of the new additions, 17 drugs were recently approved in China between January and August 2020, underscoring the NHSA’s increasing commitment to encouraging innovative drugs that address unmet needs;
- New mechanisms for NRDL inclusion and negotiation emerged, with VBP (volume based pricing) becoming another path to direct NRDL inclusion;
In October 2020, we shared our perspectives on the 2020 NRDL outlook, identifying three key themes and making five predictions. In this article, we revisit these themes and predictions, building on our ongoing monitoring of the processes and outcomes, as well as first-hand insights from industry players and key stakeholders.
Theme 1: NRDL processes evolve to include more engagements and interactivity
While this was evident and refreshing from the start of the 2020 NRDL process in August, it became clearer as the processes unfolded.
- The 2020 NRDL marks the first time in history that pharma companies submit applications for formal review;
- For the drugs shortlisted for negotiation, companies had the opportunity to meet evaluation expert panels and present their data, model, and evidence;
- The pharmacoeconomics evaluation panel consists of 40 experts nominated by healthcare security authorities and medical associations, headed by Dr. Gordon Liu, an HTA expert from PKU;
- The budget impact evaluation panel consists of 12 experts nominated by healthcare security authorities and medical associations, headed by Mr. Jie Zheng, head of the Beijing Medical Security Bureau;
- Subsequently, companies had two rounds of tendering with negotiation experts, and will proceed if tender prices do not exceed the NHSA evaluated price by 15%;
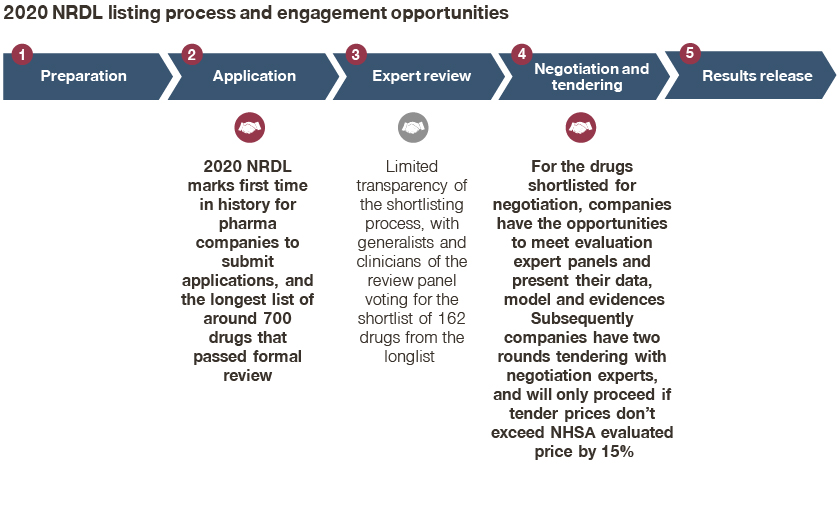
At the same time, there was limited transparency and visibility on the shortlisting process from around 700 drugs to 162 candidates, underscoring the importance of engaging review experts earlier on, and highlighting the intense competition reflected in theme 2.
Theme 2: Long list of drugs going into the NRDL translated into intense competition
After overcoming the competition to get into the shortlist, the candidates were further evaluated by separate panels on the basis of pharmacoeconomics and budget impact, and were divided into five negotiation groups that went through two rounds of price tendering.
- While the NHSA highlighted the success rate at 73% from the shortlist to the final list as an encouraging sign for the industry, the actual success rate stood at less than 20% given the long list that passed the formal review; historically the success rates stood at 82%, 94%, and 59% from the 2017-2019 negotiations;

- Price concessions averaged at 51% for the drugs that went through negotiations and made it to the 2020 final list, compared to 44%, 57%, and 61% average cuts from 2017 to 2019;

- Price concessions are more salient in some contested categories and subcategories; for example, the much followed PD-1/PD-L1s saw stiff competitions among the seven players, and the winners walked away with around 80% price cuts;
2020 NRDL negotiation outcomes: PD-1/PD-L1s
| Molecule | Company | China indications | 2020 NRDL outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nivolumab | BMS | NSCLC, head and neck, gastric cancers | not included |
| Pembrolizumab | Merck | Melanoma, NSCLC, esophageal squamous carcinoma etc. | not included |
| Durvalumab | AstraZeneca | NSCLC | not included |
| Atezolizumab | Roche | SCLC | not included |
| Camrelizumab | Hengrui | Classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma, NSCLC, HCC, esophageal squamous carcinoma etc. | 80% price cut |
| Tislelizumab | BeiGene | R/R cHL, urothelial carcinoma | ~80% price cut |
| Toriplalimab | Junshi | Melanoma | ~80% price cut |
- While the magnitude is still substantial, it is encouraging to see that the NHSA is not pursuing that as the single most important KPI for the negotiations by outdoing the price cuts from previous years;
Theme 3: Strong signal encourages innovations that address unmet needs
The NHSA made an interesting change to the NRDL formal review eligibility on August 17 2020, so all drugs approved by that date were encouraged to submit their applications. Most newly approved drugs seized the opportunity, and many were not disappointed;
- In fact, 17 drugs approved in 2020 made it to the NRDL final list, accounting for over one sixth of the 96 drugs that made it through the negotiations;
- Of the 17 newly approved drugs, three are 3 traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and the rest are western drugs across diverse therapeutic areas, including oncology, cardiovascular, immunology, antivirals, and rare diseases;
NRDL inclusion of drugs newly approved in 2020
| Drug | Indication | Company | China approval date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coblopasvir | HCV | Kawin | 2020 02 |
| Favipiravir | Flu | Hisun | 2020 02 |
| Almonertinib | EGFR T790M NSCLC | Hansoh | 2020 03 |
| Vedolizumab | UC, Crohn’s Disease | Takeda | 2020 03 |
| Avatrombopag | Thrombocytopenia | Fosun | 2020 04 |
| Tislelizumab | R/R cHL, urothelial carcinoma | BeiGene | 2020 04 |
| Siponimod | Multiple sclerosis | Novartis | 2020 05 |
| Glycopyrolate /formoterol fumarate | COPD | AstraZeneca | 2020 05 |
| Deutetrabenazine | Huntington’s | Teva | 2020 05 |
| Dupilumab | Atopic dermatitis | Sanofi | 2020 06 |
| Zanubrutinib | MCL, CLL, SLL | BeiGene | 2020 06 |
| Inetetamab | Breast cancer | 3S Bio | 2020 06 |
| Ertugliflozin | Diabetes | MSD | 2020 07 |
| Edaravone Decanol | Stroke | Simcere | 2020 07 |
| Jingu pain relief gel 筋骨止痛凝胶 | Arthritis | Kangyuan | 2020 04 |
| Lianhua cough tablet 连花清咳片 | Bronchitis | Yiling | 2020 05 |
| Sangzhi total alkaloids 桑枝总生物碱片 | T2D | Wuhe Boao | 2020 03 |
- This signals a much desired linkage between new drug approval and coverage, and represents the most encouraging gesture so far: dynamic inclusion of innovative drugs intended to address unmet clinical needs for rare diseases, chronic diseases, and critical diseases alike.
Besides the three themes we identified, Simon-Kucher made five bold predictions on the 2020 NRDL in October, and here is the readout of them.
Simon-Kucher NRDL predictions and readout summary
| Predictions | Readout |
|---|---|
1: With around 700 drugs that have made it into the 2020 NRDL process, only a small fraction will make it to the final list |
|
| 2:The seven categories stand to have very different likelihoods of NRDL inclusion reflecting NHSA priorities |
|
| 3: Price concessions will be substantial, and more so for Category V and VII |
|
| 4: Pharmacoeconomics and budget impact considerations are increasingly important in 2020 NRDL |
|
| 5: Innovative contracting models may emerge at the 2020 NRDL |
|
Please reach out to our experts to receive the full Simon-Kucher NRDL readout for an in-depth revisit of our five predictions, and score us on our hits and misses.
Furthermore, we cordially invite you to participate in our NRDL outlook survey with a few simple clicks here, and we will share with you the in-depth analysis of the aggregated results:
Take the survey now!
Read more from this series:
Part 1: Embracing the Change: 2020 China NRDL Outlook
Part 3: Embracing the Change: Strategizing on Volume-based Procurement in China
Part 4: Embracing the Change: Accessing Rare Disease Patients in China
Part 5: Embracing the Change: China Commercial Health Insurance Opportunities