Explore how cell and gene therapies (CGTs) are accessing major Asian markets. Our experts share insights on market-specific strategies and innovative reimbursement models that are shaping healthcare and driving better growth in Asia.
Cell and gene therapies (CGTs) have seen vibrant development across Asia, with nine chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) T cell therapies and four gene therapies available across major markets today. These innovative therapies have been proactively exploring different access and reimbursements approaches tailored to each market, with different levels of success to date.
To date, a total of 9 CAR-T cell therapies and 4 gene therapies have been approved in Asian markets
- Reimbursed
- Approved but not Reimbursed
- Not available / approved
| Brand | Manufacturer | Japan | South Korea | Taiwan | China | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAR-T cell therapy | Carvykti | Legend Biotech , J&J | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| Yuanruida (CNCT19) | JUVENTAS | 2023 | ||||
| Carteyva | JW Therapeutics | 2021 | ||||
| Fucaso | IASO BIO, Innovent | 2023 | ||||
| Saikaize (Zevor-cel) | Carsgen Therapeutics | 2024 | ||||
| Abecma | BMS, bluebird bio | 2022 | ||||
| Breyanzi | BMS | 2021 | ||||
| Yescarta | Kite Pharma, Fosun Kite | 2021 | 2021 | |||
| Kymriah | Novartis | 2019 | 2021 | 2021 | ||
| Gene therapy | Zolgensma | Novartis | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | |
| Collategene | AnGes | 2019 | ||||
| Luxturna | Spark Therapeutics, Novartis | 2023 | 2021 | 2022 | ||
| Delytact | Daiichi Sankyo | 2021 |
CGT in major Asian markets
Japan: Market access and reimbursement insights
Japan has approved five CAR-T cell therapies and four gene therapies since 2019, all of which have received public reimbursement after launch.
- In Japan, CGTs can be reimbursed as either pharmaceutical products or medical devices, depending on the mechanism of action (MoA) and purpose of use.
- For CGTs reimbursed as pharmaceutical products, NHI uses cost calculation or comparator pricing methodology, considering nine price premium categories:
- The pricing assessment for the first CAR-T cell therapy, Kymriah, followed the cost calculation method (i.e., price of product determined by submitted cost) and achieved a price premium reward due to orphan designation as well as novel MoA and efficacy in inadequate responders. Other CAR-T cell therapies have since used Kymriah as the comparator and achieved prices largely on par with that of Kymriah.
The pricing assessment for Zolgensma, a gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) was conducted using the comparator pricing method (i.e., price of product determined by benchmarking to similar therapies), with Spinraza as the benchmark. It managed to achieve Senkuteki and Usefulness (I) premiums at 10 percent and 50 percent, respectively.
| Category | Rationale for reward | Premium rate | Rewarded CGT drugs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price premium | Innovativeness | 70%-120% | None | |
Usefulness (I) | Clinical outcome | 35%-60% | Kymriah, Zolgensma, Luxturna | |
Usefulness (II) | Clinical outcome/ | 5%-30% | None | |
Senkuteki | Breakthrough treatment launched in Japan first-of-world | 10%-20% | Zolgensma, Delytact | |
Marketability (I) | Orphan drugs | 10%-20% | Kymriah, Delytact, Luxturna | |
Marketability (II) | Small market (i.e., therapeutic categories with market size ≤0.5% of the total ethical drug market)1 | 5% | None | |
Pediatric usability | Extra effort on pediatric use | 5%-20% | None | |
Specific use | Drugs designated for specific use | 5%-20% | None | |
Rapid launch | Designated for priority review and launched in Japan ahead of, or with minimal delay to US/Europe | 5%~10% | None |
- Early entry into the Japanese market is possible through Conditional, Time-Limited (CTL) approval (i.e., CGTs with probable clinical benefits but insufficient evidence to achieve full market authorization required for regulatory approval). CTL-approved CGTs may result in a lower price range and stricter access restrictions due to limited evidence available.
South Korea and Taiwan: Market access and reimbursement insights
South Korea and Taiwan have also been open to CGT, albeit with more caution. To date, South Korea has reimbursed one CAR-T cell therapy and two gene therapies, while Taiwan has reimbursed one CAR-T cell therapy and one gene therapy. These CGTs are eligible for public reimbursements, but they are accompanied by outcome-based agreements in both markets and installment schemes in Taiwan.
- In South Korea, three CGTs (Kymriah, Zolgensma, and Luxturna) were reimbursed via the pharmacoeconomic (PE) exemption pathway with an outcome-based risk sharing agreement (RSA), on top of the usual “Total Expenditure Cap” and “Refund” RSAs. Take the recent reimbursement case as an example:
- Luxturna first attempted to be listed by NHIS in 2021 but was not successful. It finally achieved listing in February 2024 after refining its dossier and adopting the outcome-based RSA with NHIS.
- Under the outcome-based agreement, the efficacy data will be closely monitored for the first three months and annually thereafter for a period of four years. A refund will be triggered if the outcome fails to meet the pre-defined threshold.
- Luxturna was able to qualify for the PE exemption pathway, given it is:
- An orphan drug (target patient population below 200) with no alternative treatment.
- Perceived as challenging for evidence generation.
- Listed in at least three of the A8 countries (the US, the UK, Switzerland, Japan, France, Italy, Germany, and Canada). Among these, the US, the UK, Switzerland, Japan, France, and Italy have already reimbursed Luxturna.
- Taiwan has also adopted outcome-based agreements for CGTs.
- Novartis and Taiwan NHIA entered into an outcome-based agreement for Zolgensma in 2023.
- Each patient case needs to be reviewed and approved by a special panel composed of at least two experts before reimbursement.
- Efficacy data, including CHOP-INTEND, HINE Section 2, and WHO motor milestones, need to be evaluated every four months and efficacy reports need to be issued annually for up to 10 years.
- NHIA will pay in installment based on patient’s efficacy data.
- Novartis and Taiwan NHIA entered into an outcome-based agreement for Zolgensma in 2023.
China: Market access and reimbursement insights
As the latest wave of innovative therapies, CGT has been making it way to China. To date, five CAR-T cell therapies have been launched in China, with Yescarta indicated for r/r LBCL, Carteyva for r/r LBCL and r/r FL, Yuanruida for r/r B-ALL, and Fucaso and Saikaize for r/r MM. While there has been no successful NRDL listing for CGT so far, they have all been exploring alternative access and affordability levers in the private market with resourcefulness and ingenuity.
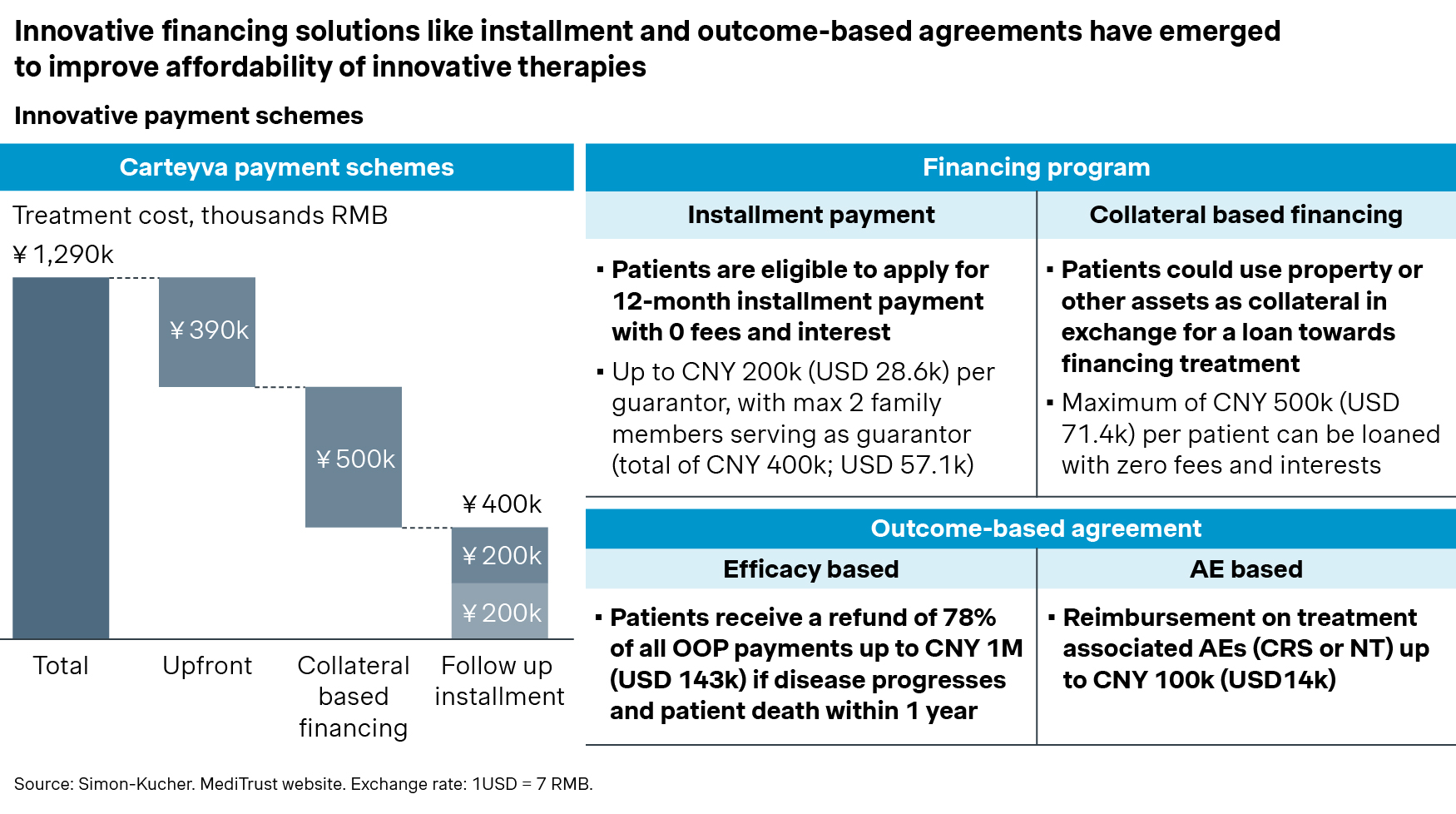
Carteyva, for example, launched innovative financing solutions that offer installments and collateral-based financing for its patients, significantly reducing their one-time out-of-pocket payments.
Additionally, Carteyva’s outcome-based insurance addresses concerns about long-term efficacy and adverse effects, offering patients up to CNY 1 million refund for disease progression within one year and CNY 100,000 for treatment-related adverse effects.
![graph 3]()
- Yescarta has also launched an installment payment program and several outcome-based insurance schemes in cooperation with insurance companies and third-party administrators.
- Yescarta’s collateral-backed financing solution allows patients to apply for a 24-month installment payment with no fees or interest.
- Yescarta also introduced Patient Assistance Program with a one-time subsidy of CNY 200,000 to further improve affordability.
- With a newly unveiled outcome-based insurance scheme, patients can receive a refund of up to CNY 600,000 if they do not achieve complete response (CR) within three months. Another insurance scheme provides a refund of up to CNY 200,000 for 3L r/r LBCL patients experiencing disease progression within three months.
- By the end of 2023, Yescarta was listed in the specialty drug formularies for over a hundred cities’ Commercial Health Insurance plans, which have been key to improve patient access and affordability in combination with other levers.
In parallel, the industry has partnered with key stakeholders like patient advocacy groups, government authorities, and payers to shape access and reimbursement policies for CGT.
China Organization for Rare Disorders (CORD), a leading patient advocacy group, recently collaborated with Simon-Kucher to publish a whitepaper on Innovative Access Solutions for Gene Therapies. The whitepaper outlined a three-step blueprint for gene therapies access in China, starting with regional pilots and gradually expanding across the nation. It included 12 concrete recommendations on optimizing CGT value assessment framework, funding pathways, and innovative payment schemes. The whitepaper has received great feedback from stakeholders across the industry and ecosystem since its release, and serves as a rallying call for better CGT access going forward.
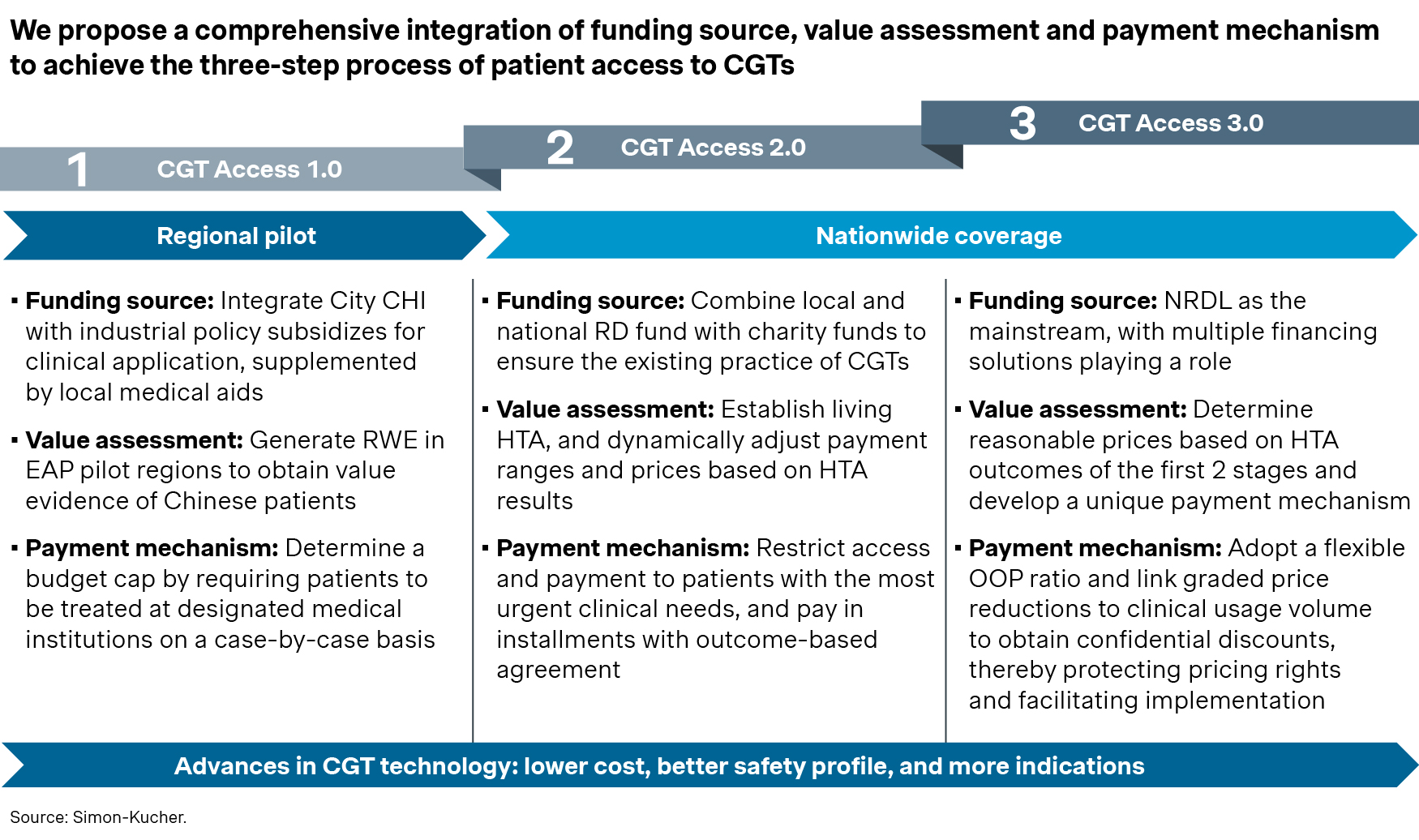
Indeed, CGT has emerged as a strategic priority for regional pilots in Beijing, Guangzhou, and Shanghai. Beijing, for example, has recently established the Tianzhu pilot zone to provide early access to innovative therapies like CGT, and introduced a number of policy initiatives for better access and reimbursements. High-profile regional pilots like this will bring a new chapter for CGT in China, and pave the ways for better access in the near future.
It is clear that the access and reimbursement environment across Asia has been changing rapidly and is expected to continue evolving.
Winning in the market requires a strategic framework to assess the potential of each market, tailor market-specific access strategies, and a forward-looking lens to prepare for future developments.
For more information, reach out to our industry experts.
Thanks to contributions by Cindy Piao!
Better Market Access
The role of better market access is to remove any hurdle that prevents or hinders patients from receiving available treatments. In the right place, and at the right time.
Today, the impact of market access spans clinical development, regional commercial activities, patient engagement, and post-launch compliance. Yet, for many pharmaceutical companies, planning for commercialization only truly begins when a drug has been submitted for approval — far too late in the process.
Get to know our insights on local trends, regional and global developments and global to local excellence.