The metaverse and its underlying technologies offer significant commercial opportunities to drive growth for insurers in both the short and long term. Successfully laying the foundations for this growth requires clarity and flexibility across four commercial growth levers: strategy, sales, marketing, and monetization.
On October 28, 2021, Facebook Inc. officially rebranded as Meta Platforms, Inc., instantly making the metaverse the hottest topic in town. A little more than 12 months later, the narrative seems to have taken a 180-degree turn, with Meta losing close to 80 percent of its market capitalization since the announcement, and the wider Web3 industry having seemingly returned to its cyclical bear market, sometimes dubbed a “crypto winter.”
The loss in market capitalization can’t be attributed entirely to the shift in focus Meta announced in 2021; other strategic and operational factors also played a role, like the iOS 14.5 update, which limited ad targeting capabilities, and the general surge in big tech equity since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a temporary spike in company valuations. However, Meta’s reversal of fortunes has led many public market participants to question its initial commitment of 10 billion US dollars and plans to hire 10,000 people over the coming years.
In the larger context though, this investment represents just a fraction of the global investment in the metaverse and its development, as well as the overall potential of what the metaverse could soon become. Investors from Google, Microsoft, Tencent, and many other companies have started pouring resources into developing the metaverse in recent years, while early users of the platforms are equally engaged and have been spending millions of their own money.
What is the metaverse?
Many works of science fiction – The Matrix, Ready Player One, and Tron to name a few – have presented visions of vast online virtual environments that extend or replace the world we all live in. The term “metaverse” itself is usually attributed to a 1992 science fiction novel.
However, recent events and technological advances have driven the term into the mainstream. Since then, a variety of definitions for the metaverse have been offered. But, defining the metaverse is a bit like hitting a moving target.
The general understanding and overall vision for the metaverse is continuously evolving, and as such, much about where we are headed remains unclear. Nevertheless, most definitions of the metaverse share a few key characteristics.
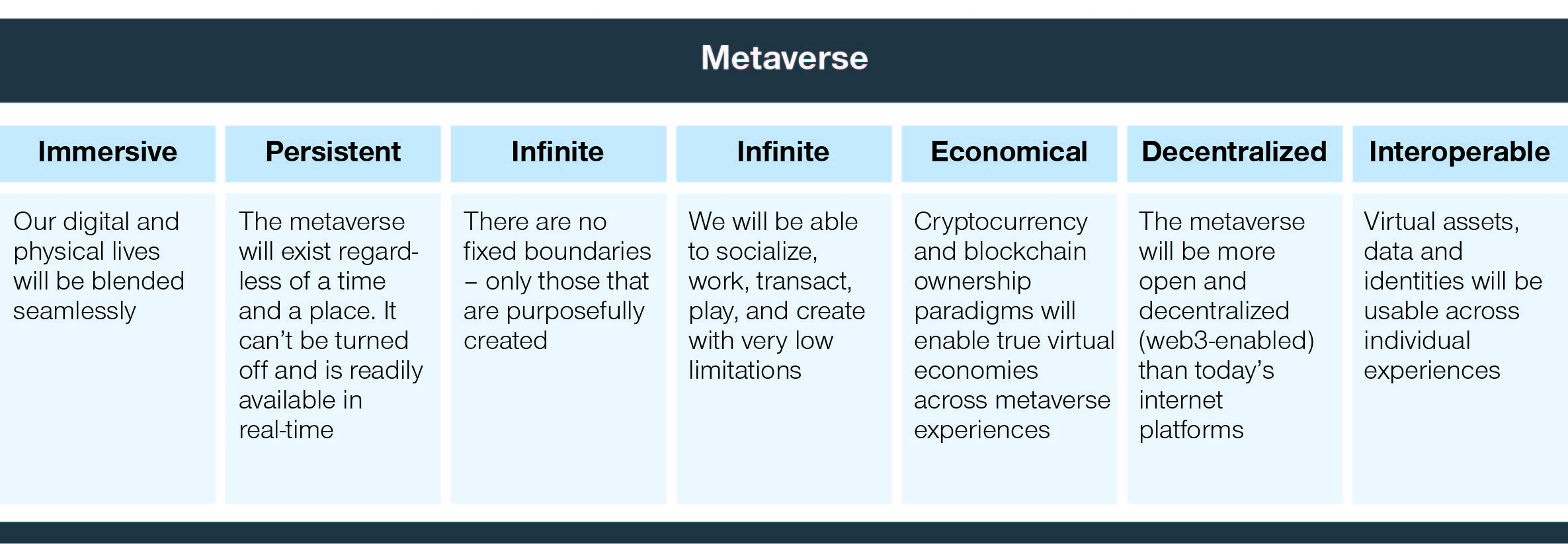
For a more detailed analysis of the metaverse’s larger impact on commercial opportunities across industries, please refer to our previous report “Unlocking the Metaverse: Commercial Opportunities in an Evolved Internet.”
What does metaverse have to do with insurance?
The commercial opportunities, both short- and long-term, created by the metaverse and the underlying technologies are significant.
Like for previous iterations of the internet, there will be no clear boundary between “before the metaverse” and “after the metaverse.” We will see a gradual transition as foundational technologies are refined and products iterated. This means that “wait-and-see” approaches, while tempting, could turn out to be damaging in the long run . Significant opportunities inherently carry an underlying risk of falling behind the market – especially if business leaders fail to acknowledge this next digital revolution and don’t act accordingly.
Successfully laying the foundations for growth in the metaverse requires clarity and flexibility across four commercial growth levers:
• Strategy
• Sales
• Marketing
• Monetization
In our report “Unlocking the Metaverse: Commercial Opportunities in an Evolved Internet,” we dive into the changes to be expected across these four key commercial growth levers and how enterprises can position themselves to succeed in this next phase of the internet.
In this report, we focus on some of the key trends across these pillars within the insurance sector. While the metaverse will have a varied impact on insurers, many of the changes in their business models and in customers’ behavior are yet to unfold, as the development and adoption of the required technology is still in its early stages.
Strategy: New business models and risk opportunities
Perhaps the largest change the metaverse is expected to bring about will be in new digital product and service offerings. The transition from a largely physical to (exclusively) digital mode of interaction is also prompting both a fundamental change in the product needs of policy holders and new experimental options in the design of governance policy design.
New product needs
The metaverse is big business. A digital artwork by Beeple sold at a Christie’s auction for 69 million dollars. Decentraland, a virtual world consisting of 90,000 real estate plots that owners can develop or lease out to others, is the largest decentralized metaverse, with a value surpassing 3 billion dollars. Another promising example is ZED Run, a virtual recreation of the horse-racing and -breeding industry that generated nearly 50 million dollars in 2021 through the trading and breeding of virtual racehorses, sometimes called “living, breathing NFTs.”
By definition, a metaverse is virtual, not physical. All the same, there are many types of assets which could exist in a metaverse:
• Cryptocurrencies
• Virtual real estate
• Digital artworks
• In-game currencies (e.g., V-Bucks in Fortnite)
• In-game tools (e.g., Minecraft Tools)
• Any virtual object that could be destroyed or damaged according to the controlling logic (and events permitted by that logic) in any realm of any metaverse, such as: automobiles, homes, businesses, health, lives.
With so much at stake, some participants in the metaverse will have a sense of ownership of, pride in, and responsibility for their virtual assets. These participants will want to mitigate the risk of losing their assets by taking out metaverse insurance – and will be willing to pay premiums that have value in the physical world. This presents a currently untapped opportunity for traditional insurers.
Sales in the metaverse world
The route-to-customer will become even more phygital (physical with digital enhancement). Insurers who position themselves to leverage the new possibilities that phygital technologies provide will outperform their direct competitors and reap the rewards that they offer.
This will affect insurers’ direct mode of interaction not just with their customers (see “Immersive sales”), but with their own agency and bancassurance sales staff as well (see “Sales training”).
Immersive sales
The COVID-19 pandemic has made alternatives to face-to-face interactions a necessity for insurance companies. Sellers can’t meet their prospects anymore due to the medical risks this contact would pose. As a result, insurance agents are now using Zoom and other collaboration tools to try and sell insurance. This is obviously a temporary solution that can never fully replace a face-to-face sales pitch. While general insurance products such as vehicle, home, and dog or cat health insurance have successfully moved to a fully digital sales experience, life insurance and other big-ticket insurance products still need that extra personal touch. The metaverse provides an opportunity to give customers a truly personal experience even in a virtual world.
Heungkuk Life Insurance, a financial subsidiary of the Taekwang Group, announced in August 2021 that it was the first life insurance company to join the Korean Metaverse Alliance, a collaboration between the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT and more than 300 national companies. As part of the move, it also announced plans to launch a “virtual advice window” within the metaverse that will allow customers to visit a branch using a virtual reality (VR) headset.
Sales training
Educating sales staff across agency and bancassurance channels represents a key pillar of sales success for all insurance organizations. Training institutes function as a key enabler in onboarding new sales staff and upskilling more senior sales team members. Traditionally these institutes conducted their training programs through in-person seminars supplemented with training materials in various written, audio, and video formats. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic, they needed to find ways to move their operations online.
While many used Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and other dedicated videoconferencing tools, Hanhwa Life introduced its own training institute within the metaverse, Lifeplus Town. Designed to reflect the architectural structure of Hanhwa Life’s physical training institute, Lifeplus Town consists of a conference hall, lecture hall, event zone, quiz zone, and cafe. Participants can move freely throughout the campus, attend events, and communicate in real-time via written messages and video chat. Hanhwa Life has been trialing the platform for sales staff and plans to expand its use.
Marketing
Throughout history, marketers and marketing functions have been quick to embrace technological shifts and leverage the capabilities that new technologies, developed by hired mobile app developers, can provide for promotional effort. It is therefore hardly surprising that many companies’ strategic efforts within the metaverse have begun with small-scale actions in marketing before spreading to other functional areas of the organization.
Within the financial services industry in particular, these marketing efforts within the metaverse have largely focused on the lead generation segment of the marketing funnel.
Lead generation
Insurers are getting really good at converting customers once they have made first contact, either via their website, a mobile app, or a sales agent. Where most insurers still struggle is making first contact. Unfortunately, the insurance industry is still very reliant on push strategies. Very few customers are actively looking for insurance products unless they’re expecting or have just experienced a major life event. Getting prospects’ eyeballs on new products is therefore always a very challenging task.
Now it is clear that future generations are going to spend a lot of time online and in virtual worlds, so why not take the product to where the customer is? Coke, KFC, Balenciaga, and Stella have already taken the step of reaching out to customers in the metaverse, and insurance companies can potentially use this space to find future Gen Z and Gen Alpha customers.
Major players in financial services have been quick to follow, with a handful of players such as J.P. Morgan, HSBC, Union Bank, and BNP Paribas launching their own (smaller-scale) efforts within the metaverse. One recent example welcomed with great fanfare was the opening of J.P. Morgan’s “Onyx Lounge” in February 2022, a virtual lounge in the blockchain-based world of Decentraland. Situated on a virtual plot of land in Decentraland, the largest 3D metaverse project on the Ethereum blockchain, users can visit this lounge with their avatars.
Once inside, users can interact with each other or find out more about J.P. Morgan’s offerings within the metaverse. To reach the Onyx Lounge, users just need to log into Decentraland through their regular web browser and then head to the coordinates 94, 21, the Metajuku district, where the Onyx Lounge will be the first thing they see.
Monetization
The underlying digital, automated, and decentralized nature of the metaverse has allowed companies to experiment with novel forms of monetization using new options in the design of governance policy.
Smart contract technology, with its ability to dictate contract terms between parties, monitor key contract parameters in real time, and enforce contract outcomes in an automated and effectively scalable way, has made it possible to conceive of new services to offer.
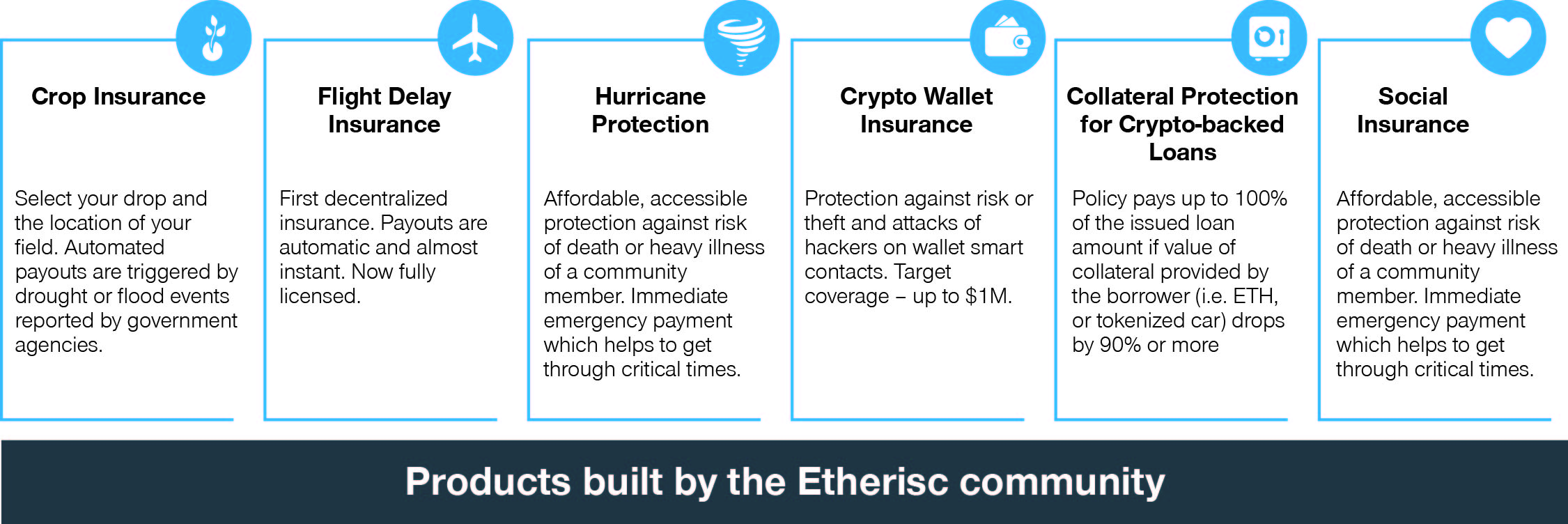
Start-ups like Etherisc, a decentralized insurance protocol on the Ethereum blockchain that has developed a series of novel smart-contract insurance policies, are some of the most prominent examples of new developments in the industry taking advantage of new options in governance policy design. The start-up offers six distinct products, all built on a smart contract foundation that enables automated payouts as events (e.g., flight delay information, flood events) are triggered via blockchain oracles (decentralized verified data providers). Etherisc’s smart contract products include crop insurance, flight delay insurance, hurricane protection, crypto wallet insurance, collateral protection for crypto-backed loans, and social insurance.
Is the insurance sector ready for the metaverse?
COVID-19 has changed the world in many aspects, and things may never be the same. Despite this, insurance (especially life insurance) remains stuck in the old ways of working. With a very traditional approach of selling products through intermediaries and requiring a lot of paperwork to complete an application, insurance is just as hard to understand and purchase today as it was 10 years ago. But change is on the horizon. Insurers are finally making major investments in digitalization. Unfortunately, these investments are largely aimed at catching up with what other industries have already achieved, and what customers have come to expect from organizations they interact with on a daily basis. In short, insurers need to look beyond just competing with other insurers and start really investing in meeting the needs of future customers.
How to get started in metaverse?
It is difficult to predict the future of the metaverse at this point. But the monetization and growth opportunities across the insurance and financial services sectors are substantial. Every industry, from entertainment to education and healthcare, will be affected in one way or another.
As more use cases are created, and the technology becomes more accessible, the metaverse will become a key revenue source for many individuals, brands, and creators who understand the growth opportunities it presents. Increased adoption will drive growth, in turn increasing the benefit to all the parties invested in the metaverse’s success, including the developers who build it, the brands that monetize it, and the users who enjoy it.
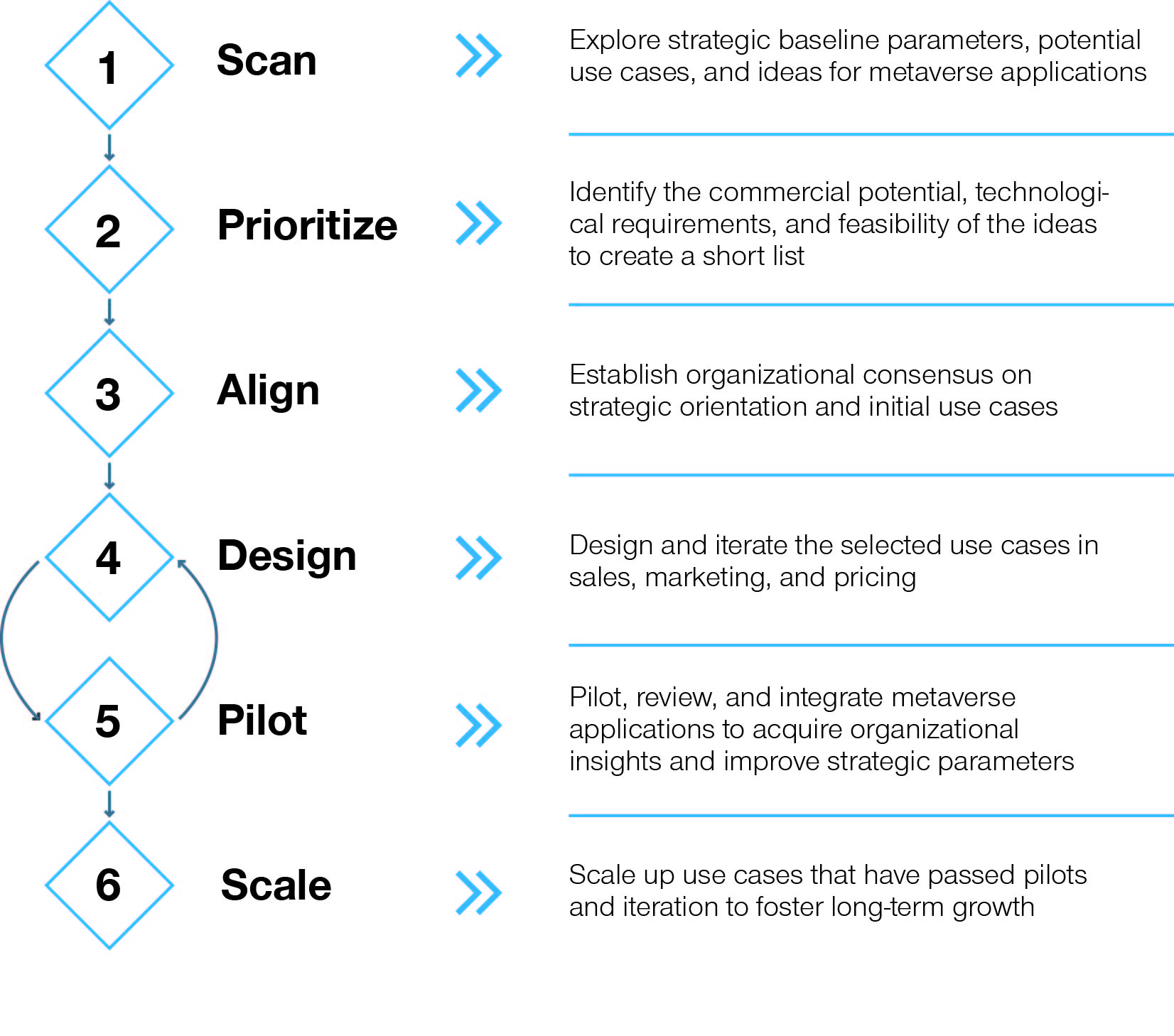
To be ready for the changes that will be brought about by the continuous growth of the metaverse, insurers should start exploring and implementing elements of a metaverse strategy today. We suggest a six-step approach to get started and establish a foundation for an overarching strategy.
Simon-Kucher & Partners: Unlocking sustainable growth in a phygital world
With a talented team of experts across industries, growth levers, and technological fields, Simon-Kucher is ideally placed to support companies to act on metaverse growth opportunities.
Over 30 years of experience in unlocking short- and long-term growth helps us deliver clear, tangible benefits across strategy, sales, marketing, and monetization applications. Using our consulting teams’ in-depth industry knowledge, sophisticated market testing and advanced analytics conducted by trained researchers at Simon-Kucher Elevate, and powerful digital applications built by our Simon-Kucher Engine team of design and development experts, Simon-Kucher offers clients a holistic solution that meets their needs.








